| CSC403: Fields and methods [4/9] |    |
Local variables are stored in method invocations. Fields are stored in objects.
Fields are sometimes called member variables or instance variables.
01 |
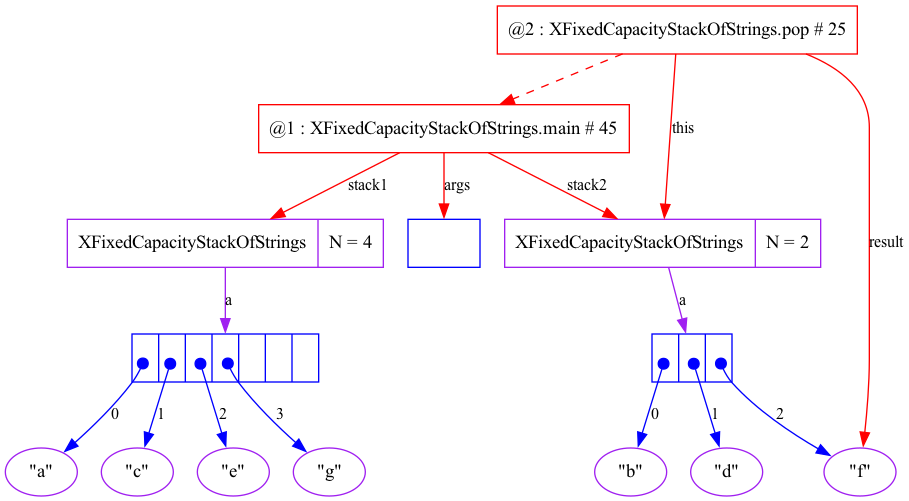
package algs13; import stdlib.*; public class XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings { private String[] a; // holds the items private int N; // number of items in stack // Invariant (after the constructor): // a[0]..a[N-1] are non null // a[N]..a[a.length-1] are null public XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (int capacity) { this.a = new String[capacity]; this.N = 0; } public int size () { return N; } public boolean isEmpty () { return (N == 0); } public void push (String item) { if (item == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException (); if (N >= a.length) throw new RuntimeException ("Stack full"); a[N] = item; N++; } public String pop () { if (N <= 0) throw new RuntimeException ("Stack empty"); N--; String result = a[N]; a[N] = null; return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { //Trace.showObjectIdsRedundantly (true); Trace.showBuiltInObjects(true); //Trace.drawStepsOfMethod ("main"); Trace.drawSteps (); Trace.run (); XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings stack1 = new XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (7); XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings stack2 = new XFixedCapacityStackOfStrings (3); stack1.push ("a"); stack2.push ("b"); stack1.push ("c"); stack2.push ("d"); stack1.push ("e"); stack2.push ("f"); stack1.push ("g"); while (!stack2.isEmpty()) { StdOut.println (stack2.pop ()); } StdOut.println(); while (!stack1.isEmpty()) { StdOut.println (stack1.pop ()); } } } |