SE450: Lecture 4
(Structural Patterns)
-
You have one and a half hours to take the exam.
-
If a question is unclear or
ambiguous, write down your assumptions.
-
The exam is closed book and closed notes.
-
You may consult one letter-size page (front and back) of
notes that you have prepared.
-
Write your answers on the exam.
If I can not read your answer clearly, it will be marked as
incorrect.
-
You will find some information on Java APIs, junit, and design
patterns at the end of the exam.
-
When drawing UML class diagrams, follow these guidelines:
- Be specific (prefer aggregation and dependency to association, prefer
composition to aggregation).
- Show mutiplicities on aggregations and compositions.
- Be careful with arrowheads and with dashed/solid lines.
- Clearly distinguish classes and interfaces.
- Clearly indicate static classes.
Here is a syllabus for the exam.
+ UML Object Diagrams
- objects (fields with value)
- relations
* link
+ UML Sequence Diagrams
- objects (lifetime) (also static classes)
- method/constructor call (lifetime and arguments)
- method/constructor return (value)
+ UML Class Diagrams
- classes (fields and methods with type and visibility)
- interfaces (methods with type and visibility)
- big arrow relations (triangular arrowhead)
* specialization
* realization
- small arrow relations
* aggregation
* composition
* dependency
+ Simple Idioms and OO programming techniques (using java)
- packages
- interfaces
- classes
- constructors
- delegation
- inner classes
- static versus object classes
- immutable data classes
- mutable data classes
- data object methods (equals, hashCode, compareTo, ...)
- collection classes
+ Patterns
- static factory
- builder
- command
- strategy
- state
- composite
Interface: Primitive for describing the type
or interface of an object.
Class: Primitive for describing implementation of an
object.
Constructor: Primitive construct for building
objects.
Delegation: (Partial) responsibility for a message is
given to another object.
Subclassing: (Partial) responsibility for a message
is given to a class other than the actual class of the
object.
[Not covered on midterm, except with respect to
Object]
Immutable Data Class: Unchanging data (eg, String).
Mutable Data Class: Changing data (eg, an Employee
class that contains salary information).
Collection Class: A collection. May be mutable or
immutable.
MVC lite: Separate IO from business logic.
Static Class: A set of global variables and
functions.
Static Factory: a static class whose purpose is to
generate instances of an interface (or interfaces). The
interface and factory are public, but the implementing
classes are not.
Builder: A mutable object used to build an immutable
object. Add pieces to the builder gradually, then convert
to its immutable representation (eg, StringBuilder).
Command: Encapsulate a function as an object. The
command can then be accessed from many places. It may also
support undo/redo.
Strategy: Encapsulate variation into a separate
object. A method accesses the variation (strategy) by
delegating to a field or parameter.
State: Create the illusion that an object changes
its actual type (using delegation to a field). A nice way
to eliminate case statments.
Composite: Make collections of objects have the same
interface as single objects.
Allow collections to be treated the same as single objects.
Define a typed tree.
Here is an object diagram from the GOF:
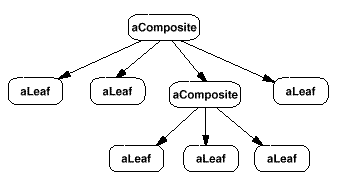
Here is a class diagram from the GOF:
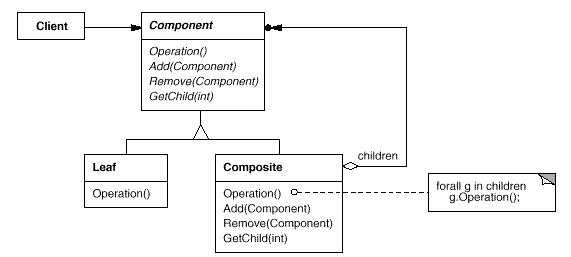
Here is an object diagram from the GOF:
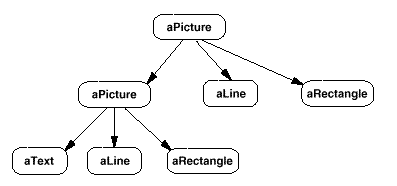
Here is a class diagram from the GOF:
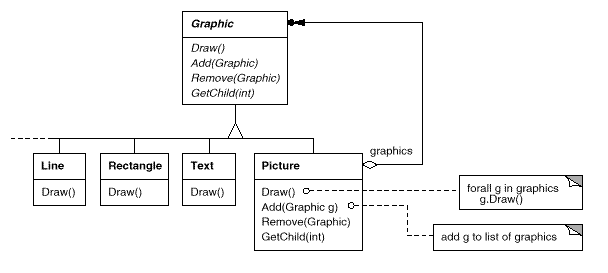
I will discuss
these notes.
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
|
package composite.one;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Expr one = new Const(1);
Expr onePtwo = new Plus (new Const(1), new Const(2));
Expr threeMfour = new Mult (new Const(3), new Const(4));
Expr m = new Minus (onePtwo, threeMfour);
Expr n = new Quot (m, new Const(5));
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println("Value: " + n.eval());
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
|
package composite.one;
public interface Expr {
int eval();
}
final class Const implements Expr {
private final int v;
public Const(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
public int eval() {
return v;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(v);
}
}
final class Plus implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Plus(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() + r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " +";
}
}
final class Minus implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Minus(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() - r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " -";
}
}
final class Mult implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Mult(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() * r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " *";
}
}
final class Quot implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Quot(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() / r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " /";
}
}
|
|
|
-
Using a static factory
-
Refactor to strategy (binary operations all have same form)
-
nary ops. What if
Plus and
Mult take any number of operands? Need an
add method on the composite.
-
Using Builder for nary ops
-
Mutable Composites
-
put
add in interface
-
use two interfaces
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
package composite.two;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Expr one = ExprFactory.newConst(1);
Expr onePtwo = ExprFactory.newPlus
(ExprFactory.newConst(1), ExprFactory.newConst(2));
Expr threeMfour = ExprFactory.newMult
(ExprFactory.newConst(3), ExprFactory.newConst(4));
Expr m = ExprFactory.newMinus (onePtwo, threeMfour);
Expr n = ExprFactory.newQuot (m, ExprFactory.newConst(5));
System.out.println(n);
System.out.println("Value: " + n.eval());
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
|
package composite.two;
public interface Expr {
int eval();
}
|
|
|
|
001
002
003
004
005
006
007
008
009
010
011
012
013
014
015
016
017
018
019
020
021
022
023
024
025
026
027
028
029
030
031
032
033
034
035
036
037
038
039
040
041
042
043
044
045
046
047
048
049
050
051
052
053
054
055
056
057
058
059
060
061
062
063
064
065
066
067
068
069
070
071
072
073
074
075
076
077
078
079
080
081
082
083
084
085
086
087
088
089
090
091
092
093
094
095
096
097
098
099
100
101
102
103
104
|
package composite.two;
public class ExprFactory {
private ExprFactory() {}
static public Expr newConst(int v) {
return new Const(v);
}
static public Expr newPlus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new Plus(l, r);
}
static public Expr newMinus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new Minus(l, r);
}
static public Expr newMult(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new Mult(l, r);
}
static public Expr newQuot(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new Quot(l, r);
}
private static class Const implements Expr {
private final int v;
public Const(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
public int eval() {
return v;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(v);
}
}
private static class Plus implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Plus(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() + r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " +";
}
}
private static class Minus implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Minus(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() - r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " -";
}
}
private static class Mult implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Mult(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() * r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " *";
}
}
private static class Quot implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
public Quot(Expr l, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return l.eval() / r.eval();
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " /";
}
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
package composite.three;
public class ExprFactory {
private ExprFactory() {}
static public Expr newConst(int v) {
return new Const(v);
}
static public Expr newPlus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpAdd(), r);
}
static public Expr newMinus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpSub(), r);
}
static public Expr newMult(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpMul(), r);
}
static public Expr newQuot(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpDiv(), r);
}
private static final class Const implements Expr {
private final int v;
public Const(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
public int eval() {
return v;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(v);
}
}
private static final class BinOp implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
private final Op op;
public BinOp(Expr l, Op op, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (op == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.op = op;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return op.run(l.eval(), r.eval());
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " " + op.toString();
}
}
private static interface Op {
public abstract int run(int x, int y);
}
private static final class OpAdd implements Op {
public String toString() { return "+"; }
public int run(int x, int y) { return x+y; }
}
private static final class OpSub implements Op {
public String toString() { return "-"; }
public int run(int x, int y) { return x-y; }
}
private static final class OpMul implements Op {
public String toString() { return "*"; }
public int run(int x, int y) { return x*y; }
}
private static final class OpDiv implements Op {
public String toString() { return "/"; }
public int run(int x, int y) { return x/y; }
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
package composite.three;
public class ExprFactory2 {
private ExprFactory2() {}
static public Expr newConst(int v) {
return new Const(v);
}
static public Expr newPlus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new PlusOp(l, r);
}
// static public Expr newMinus(Expr l, Expr r) {
// return new BinOp(l, new OpSub(), r);
// }
// static public Expr newMult(Expr l, Expr r) {
// return new BinOp(l, new OpMul(), r);
// }
// static public Expr newQuot(Expr l, Expr r) {
// return new BinOp(l, new OpDiv(), r);
// }
private static final class Const implements Expr {
private final int v;
public Const(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
public int eval() {
return v;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(v);
}
}
private static abstract class BinOp implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
private final String opString;
public BinOp(Expr l, String opString, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
this.opString = opString;
}
protected abstract int run (int x, int y);
// to be template method, there must a template method
// template method = method of abstract class, that calls an abstract method
public int eval() {
return this.run(l.eval(), r.eval());
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " " + opString;
}
}
private static final class PlusOp extends BinOp {
public PlusOp(Expr l, Expr r) { super (l, "+", r); }
public int run(int x, int y) { return x+y; }
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package composite.four;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Expr onePtwo = ExprFactory.newPlus
(ExprFactory.newConst(1), ExprFactory.newConst(2));
ExprBuilder eb = ExprFactory.newMultBuilder();
eb.add(ExprFactory.newConst(3));
eb.add(ExprFactory.newConst(4));
eb.add(onePtwo);
Expr multiplies = eb.toExpr();
Expr m = ExprFactory.newMinus (onePtwo, multiplies);
System.out.println(m);
System.out.println("Value: " + m.eval());
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
|
package composite.four;
public interface ExprBuilder {
Expr toExpr();
void add(Expr e);
}
|
|
|
|
001
002
003
004
005
006
007
008
009
010
011
012
013
014
015
016
017
018
019
020
021
022
023
024
025
026
027
028
029
030
031
032
033
034
035
036
037
038
039
040
041
042
043
044
045
046
047
048
049
050
051
052
053
054
055
056
057
058
059
060
061
062
063
064
065
066
067
068
069
070
071
072
073
074
075
076
077
078
079
080
081
082
083
084
085
086
087
088
089
090
091
092
093
094
095
096
097
098
099
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
|
package composite.four;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class ExprFactory {
private ExprFactory() {}
static public Expr newConst(int v) {
return new Const(v);
}
static public Expr newPlus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpAdd(), r);
}
static public Expr newMinus(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpSub(), r);
}
static public Expr newMult(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpMul(), r);
}
static public Expr newQuot(Expr l, Expr r) {
return new BinOp(l, new OpDiv(), r);
}
static public ExprBuilder newPlusBuilder() {
return new NaryOpBuilder(new OpAdd(), new Const(0));
}
static public ExprBuilder newMultBuilder() {
return new NaryOpBuilder(new OpMul(), new Const(1));
}
}
final class Const implements Expr {
private final int v;
public Const(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
public int eval() {
return v;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(v);
}
}
final class BinOp implements Expr {
private final Expr l;
private final Expr r;
private final Op op;
public BinOp(Expr l, Op op, Expr r) {
if ((l == null) || (op == null) || (r == null)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.op = op;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public int eval() {
return op.eval(l.eval(), r.eval());
}
public String toString() {
return l.toString() + " " + r.toString() + " " + op.toString();
}
}
final class NaryOp implements Expr {
private final Expr[] args;
private final Expr zero;
private final Op op;
public NaryOp(Expr[] args, Op op, Expr zero) {
// Don't need to test these, since the builder checks them.
// if ((args == null) || (op == null) || (zero == null))
// throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++)
// if (args[i] == null)
// throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.op = op;
this.args = args;
this.zero = zero;
}
public int eval() {
int result = zero.eval();
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++)
result = op.eval(result, args[i].eval());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++) {
sb.append(args[i].toString());
if (i+1<args.length)
sb.append(", ");
}
sb.append("]");
sb.append(op.toString());
sb.append(" ");
return sb.toString();
}
}
final class NaryOpBuilder implements ExprBuilder {
private final List<Expr> args;
private final Expr zero;
private final Op op;
public NaryOpBuilder(Op op, Expr zero) {
if ((op == null) || (zero == null))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.args = new LinkedList<Expr>();
this.op = op;
this.zero = zero;
}
public void add(Expr e) {
if (e == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
args.add(e);
}
public Expr toExpr() {
return new NaryOp(args.toArray(new Expr[0]), op, zero);
}
}
interface Op {
public abstract int eval(int x, int y);
}
final class OpAdd implements Op {
public String toString() { return "+"; }
public int eval(int x, int y) { return x+y; }
}
final class OpSub implements Op {
public String toString() { return "-"; }
public int eval(int x, int y) { return x-y; }
}
final class OpMul implements Op {
public String toString() { return "*"; }
public int eval(int x, int y) { return x*y; }
}
final class OpDiv implements Op {
public String toString() { return "/"; }
public int eval(int x, int y) { return x/y; }
}
|
|
|
Remember the awful finite state machine from Homework 3?
file:Control.java [source] [doc-public] [doc-private]
Here is a version refactored to the state pattern:
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
package state.ui.main;
import state.ui.UI;
import state.ui.UIMenu;
import state.ui.UIMenuBuilder;
class Control {
final State EXITED;
final State EXIT;
private State state;
Control(UI ui) {
EXITED = new ExitedState();
EXIT = new ExitState(this,ui);
state = EXIT;
}
void run() {
while (state != EXITED) {
state = state.run();
}
}
}
interface State {
public State run();
}
final class ExitedState implements State {
public State run() {
return this;
}
}
final class ExitState implements State {
Control control;
UI ui;
UIMenu m;
ExitState(Control control, UI ui) {
this.control = control;
this.ui = ui;
UIMenuBuilder mb;
mb = new UIMenuBuilder();
//mb.add("Default", new UIMenuAction() { public Object run() {return this;} });
mb.add("Default", () -> this);
mb.add("Yes", () -> control.EXITED);
mb.add("No", () -> control.EXIT);
this.m = mb.toUIMenu("Are you sure you want to exit?");
}
public State run() {
return (State) ui.processMenu(m);
}
}
|
|
|
Full code:
dir:state/ui [source]
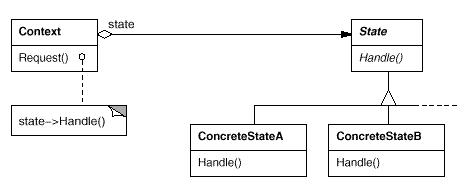
Discuss intrinsic/extrinsic state
and field/parameter refactorings.
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
package state.one;
interface I {
public int f();
public int g();
public void changeDirection();
}
class C implements I {
private boolean state;
private int i;
private int j;
public int f() {
if (state)
i += 26;
else
i -= 32;
return i;
}
public int g() {
if (state)
j += 42;
else
j -= 27;
return j;
}
public void changeDirection() {
state = !state;
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
package state.five;
interface I {
public int f();
public int g();
public void changeDirection();
}
class C implements I {
private State state = new StateMinus();
private int i;
private int j;
public int f() {
return state.f();
}
public int g() {
return state.g();
}
public void changeDirection() {
state = state.next();
}
interface State {
public int f();
public int g();
public State next();
}
class StateMinus implements State {
public int f() {
i -= 32;
return i;
}
public int g() {
j -= 27;
return j;
}
public State next() {
return new StatePlus();
}
}
class StatePlus implements State {
public int f() {
i += 26;
return i;
}
public int g() {
j += 42;
return j;
}
public State next() {
return new StateMinus();
}
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package state.four;
interface I {
public int f();
public int g();
public void changeDirection();
}
class C implements I {
private CState state = new CStateMinus(this);
int i;
int j;
public int f() {
return state.f();
}
public int g() {
return state.g();
}
public void changeDirection() {
state = state.next();
}
}
interface CState {
public int f();
public int g();
public CState next();
}
class CStateMinus implements CState {
C x;
CStateMinus(C x) { this.x = x; }
public int f() {
x.i -= 32;
return x.i;
}
public int g() {
x.j -= 27;
return x.j;
}
public CState next() {
return new CStatePlus(x);
}
}
class CStatePlus implements CState {
C x;
CStatePlus(C x) { this.x = x; }
public int f() {
x.i += 26;
return x.i;
}
public int g() {
x.j += 42;
return x.j;
}
public CState next() {
return new CStateMinus(x);
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package state.two;
interface I {
public int f();
public int g();
public void changeDirection();
}
class C implements I {
private CState[] states = new CState[] { new CStateMinus(), new CStatePlus() };
private int index;
int i;
int j;
public int f() {
return states[index].f(this);
}
public int g() {
return states[index].g(this);
}
public void changeDirection() {
index = (index+1) % 2;
}
}
interface CState {
public int f(C x);
public int g(C x);
}
class CStateMinus implements CState {
public int f(C x) {
x.i -= 32;
return x.i;
}
public int g(C x) {
x.j -= 27;
return x.j;
}
}
class CStatePlus implements CState {
public int f(C x) {
x.i += 26;
return x.i;
}
public int g(C x) {
x.j += 42;
return x.j;
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package state.three;
interface I {
public int f();
public int g();
public void changeDirection();
}
class C implements I {
private CState state = CState.MINUS;
int i;
int j;
public int f() {
return state.f(this);
}
public int g() {
return state.g(this);
}
public void changeDirection() {
state = (state==CState.MINUS) ? CState.PLUS : CState.MINUS;
}
}
|
|
|
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
package state.three;
interface CState {
public int f(C x);
public int g(C x);
public static final CState MINUS = new CStateMinus();
public static final CState PLUS = new CStatePlus();
}
class CStateMinus implements CState {
public int f(C x) {
x.i -= 32;
return x.i;
}
public int g(C x) {
x.j -= 27;
return x.j;
}
}
class CStatePlus implements CState {
public int f(C x) {
x.i += 26;
return x.i;
}
public int g(C x) {
x.j += 42;
return x.j;
}
}
|
|
|
Revised: 2008/02/12 20:46




