


| CSC300: Objects and equality [1/24] |    |
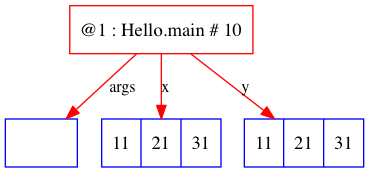
int[] x = new int[] { 11, 21, 31 }; int[] y = new int[] { 11, 21, 31 }; x=[I@8807e25, y=[I@2a3046da x=[11, 21, 31], y=[11, 21, 31] x==y : false Objects.equals(x,y) : false x.equals(y) : false Arrays.equals(x,y) : true |
|
01 |
package algs12; import stdlib.*; import java.util.*; public class Hello { public static void main (String[] args) { Trace.showBuiltInObjects (true); Trace.run (); int[] x = new int[] { 11, 21, 31 }; int[] y = new int[] { 11, 21, 31 }; Trace.draw (); StdOut.println ("x=" + x + ", y=" + y); StdOut.println ("x=" + Arrays.toString(x) + ", y=" + Arrays.toString(y)); StdOut.println (" x==y : " + (x == y)); StdOut.println (" Objects.equals(x,y) : " + (Objects.equals(x,y))); StdOut.println (" x.equals(y) : " + (x.equals(y))); StdOut.println (" Arrays.equals(x,y) : " + (Arrays.equals(x,y))); } } |